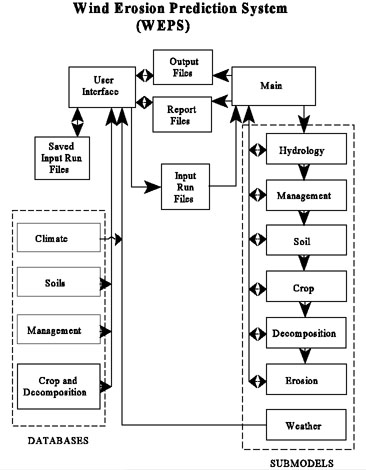

The inputs to the science model reside in a series of ASCII input run files (projects). These input files are: a Windgen file, a Cligen file, an initial field conditions file, a management file, and a run file. The science model can be executed from the command line or the interface. When WEPS is executed, the science model reads the input files, accesses necessary databases, calls each submodel daily and performs the simulation, and writes output files. The output is written to one or more ASCII files. Building the input files by hand, executing the model on the command line, and interpreting the science model output filesdirectly is possible. However, it can be time consuming and confusing. The WEPS User Interface simplifies this process.
The WEPS User Interface is written in Java. The interface can be thought of as a 'shell' or 'wrapper' around the science model which does not affect the execution of the science model. Through the interface program, the user can easily enter the information necessary to create and edit the input files. A description of how to enter this information is given in How to Operate WEPS. Once the field, location, soil, and management are described, pressing the 'Run' button performs a series of commands to execute the science model. The interface first calls the Cligen and Windgen weather generators which create the Windgen and Cligen files for the simulation. Then the WEPS science model is called and executed as described above. When the science model is finished, the interface reads and displays the selected output reports.